Eureka Math Geometry Module 2 embarks on an extraordinary journey into the realm of geometry, inviting learners to delve into the captivating world of shapes, angles, and transformations. With its engaging approach and real-world applications, this module promises an adventure that will ignite mathematical curiosity and deepen understanding.
From exploring the intricacies of similar triangles and trigonometry to unraveling the mysteries of circles and their properties, Eureka Math Geometry Module 2 provides a comprehensive and interactive learning experience. Its emphasis on hands-on activities and problem-solving challenges fosters a deep appreciation for the beauty and practicality of geometry.
Module Overview
Eureka Math Geometry Module 2 is designed to enhance students’ understanding of angles, triangles, and quadrilaterals.
The module aims to develop students’ ability to:
- Identify and classify angles
- Understand the relationships between angles in triangles and quadrilaterals
- Solve problems involving angle measures
li>Use properties of triangles and quadrilaterals to solve problems
Mathematical Practices, Eureka math geometry module 2
The module emphasizes the following mathematical practices:
- Reasoning and Proof
- Modeling and Application
- Communicating Reasoning
Unit 1: Similarity, Right Triangles, and Trigonometry
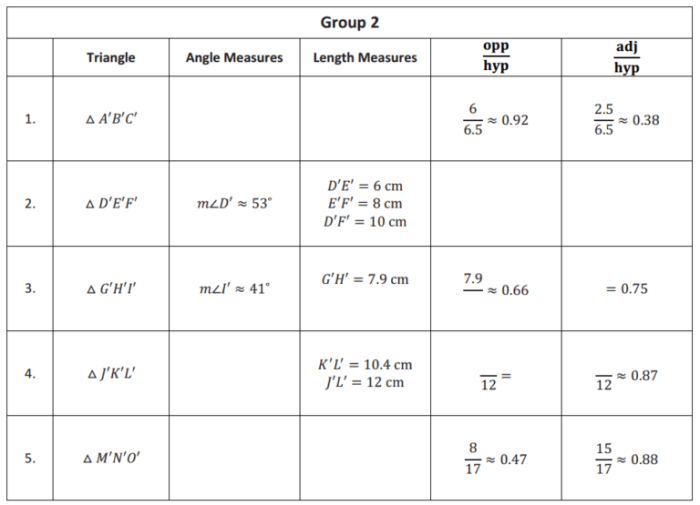
Unit 1 delves into the fundamental concepts of similarity, right triangles, and trigonometry. These concepts are intricately intertwined and provide a powerful toolkit for solving a wide range of geometrical problems and real-world applications.
Similarity involves understanding the relationships between shapes and their corresponding dimensions. Right triangles, with their unique 90-degree angles, serve as a cornerstone for trigonometry, which introduces the sine, cosine, and tangent functions to measure angles and calculate unknown sides of triangles.
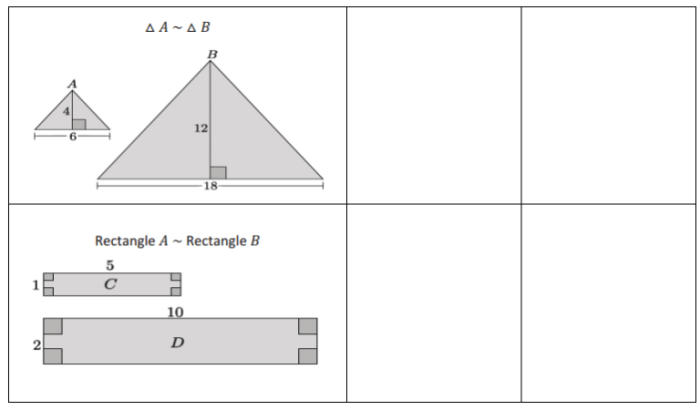
Similarity
- Similar figures have the same shape but may differ in size.
- The ratio of corresponding sides of similar figures is constant.
- Similarity transformations (translations, rotations, reflections, dilations) preserve the shape and angles of figures.
Right Triangles
- A right triangle contains one 90-degree angle.
- The Pythagorean theorem relates the lengths of the sides of a right triangle: a2+ b2= c2, where cis the length of the hypotenuse.
- The trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, tangent) are defined for acute angles in right triangles.
Trigonometry
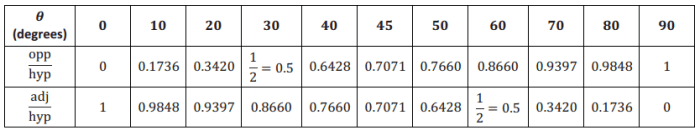
- Trigonometry uses the trigonometric ratios to find unknown angles or sides of right triangles.
- The sine, cosine, and tangent functions are defined as:
sin(θ) = opposite/hypotenuse, cos( θ) = adjacent/hypotenuse, tan( θ) = opposite/adjacent
- Trigonometry has numerous applications in fields such as surveying, navigation, and architecture.
Unit 2: Circles
Circles are fundamental geometric shapes that possess unique properties and applications across various fields. This unit delves into the study of circles, their characteristics, and their practical uses.
Key concepts explored in this unit include:
- Definition and properties of circles (center, radius, diameter, circumference)
- Relationships between angles and arcs
- Inscribed and circumscribed circles
- Tangents and secants
- Similarity of circles
Understanding these concepts enables students to solve problems involving circles, such as:
- Calculating the circumference, area, and volume of circles and spheres
- Determining the measure of central angles, inscribed angles, and angles formed by secants and tangents
- Solving problems related to the similarity of circles
Applications of Circles
Circles have wide-ranging applications in various fields, including:
- Engineering:Design of gears, wheels, bearings, and other mechanical components
- Architecture:Construction of domes, arches, and circular structures
- Navigation:Determining distances and directions using compasses and protractors
- Sports:Balls used in games such as basketball, soccer, and tennis
- Medicine:Imaging techniques like MRI and CT scans utilize circular shapes
Unit 3: Surface Area and Volume
Unit 3 of Geometry Module 2 delves into the concepts of surface area and volume, providing a comprehensive understanding of these essential geometric measurements.
Surface Area
Surface area refers to the total area of all surfaces of a three-dimensional object. It plays a crucial role in determining the amount of material needed to cover or paint an object.
- For a rectangular prism, the surface area is calculated by adding the areas of all six faces (2 x length x width + 2 x length x height + 2 x width x height).
- For a cylinder, the surface area consists of the area of the curved surface (2 x π x radius x height) and the areas of the two circular bases (2 x π x radius²).
- For a sphere, the surface area is given by the formula 4 x π x radius².
Volume
Volume measures the amount of space occupied by a three-dimensional object. It is essential for determining the capacity or storage space of containers.
Eureka Math Geometry Module 2 delves into the intricacies of geometric shapes and their properties. If you’re looking for a break from geometry, why not take a detour to Maycomb, Alabama, with our to kill a mockingbird quiz ? Test your knowledge of Harper Lee’s classic novel and return refreshed to tackle the complexities of Module 2.
- For a rectangular prism, the volume is calculated by multiplying the length, width, and height.
- For a cylinder, the volume is determined by multiplying the base area (π x radius²) by the height.
- For a sphere, the volume is given by the formula (4/3) x π x radius³.
Applications
Surface area and volume find applications in various real-world situations, including:
- Calculating the amount of paint or wallpaper needed to cover a room.
- Determining the capacity of storage tanks or containers.
- Estimating the amount of material required for construction projects.
- Understanding the design and efficiency of engines and turbines.
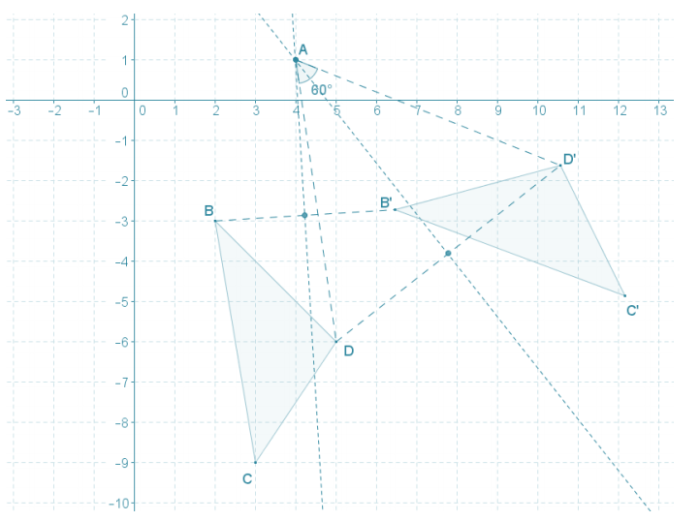
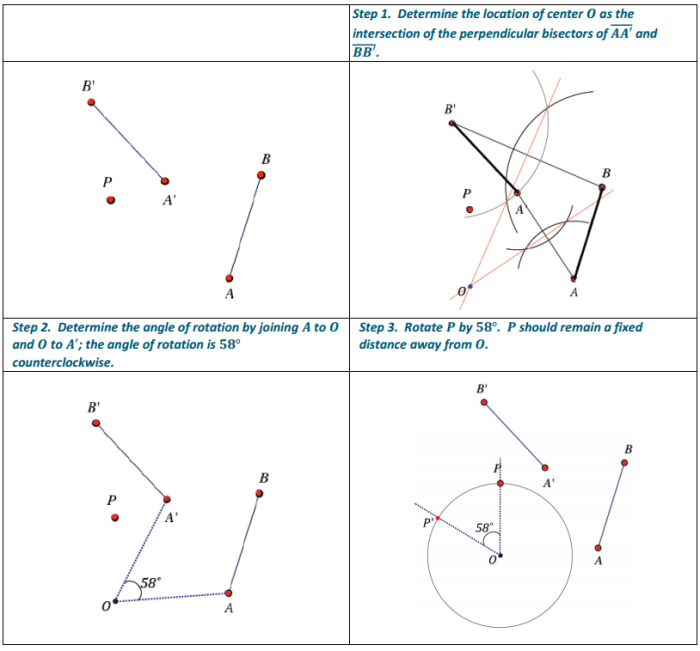
Unit 4: Transformations: Eureka Math Geometry Module 2
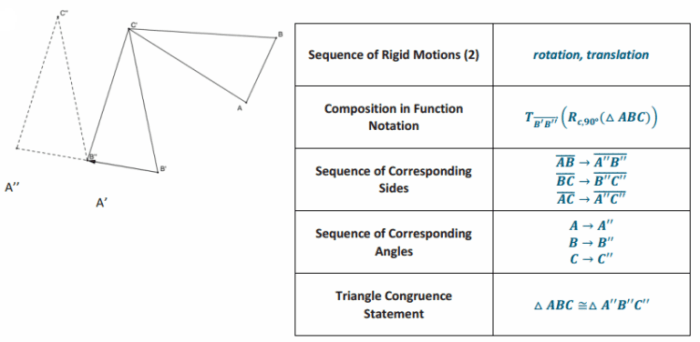
Unit 4 delves into the captivating world of transformations, where shapes undergo a magical metamorphosis. These transformations are the foundation of creating new and intricate designs in art, engineering, and various other disciplines.
Types of Transformations
- Translation:Shifting a shape from one point to another without changing its size or shape.
- Rotation:Turning a shape around a fixed point by a specified angle.
- Reflection:Flipping a shape over a line, creating a mirror image.
- Dilation:Enlarging or shrinking a shape by a certain factor, maintaining its shape.
Applications of Transformations
Transformations find practical applications in diverse fields:
- Art:Creating patterns, designs, and illusions in paintings, sculptures, and architecture.
- Design:Developing logos, graphics, and product designs with symmetry and balance.
- Engineering:Designing bridges, buildings, and machines with optimal strength and efficiency.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the main goal of Eureka Math Geometry Module 2?
Eureka Math Geometry Module 2 aims to develop students’ understanding of geometry through hands-on activities, problem-solving challenges, and real-world applications.
How does Eureka Math Geometry Module 2 approach learning?
Eureka Math Geometry Module 2 utilizes an inquiry-based approach, encouraging students to actively engage with the material, make conjectures, and justify their reasoning.
What are some of the key concepts covered in Eureka Math Geometry Module 2?
Key concepts covered in Eureka Math Geometry Module 2 include similarity, right triangles, trigonometry, circles, surface area, volume, and transformations.