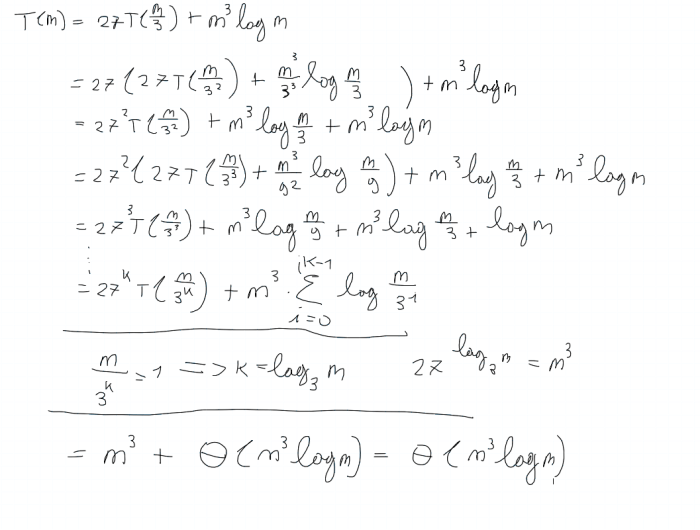Draw all resonance structures for the nitryl fluoride molecule no2f – Draw all resonance structures for the nitryl fluoride molecule (NO2F), a captivating journey into the realm of molecular resonance. This endeavor unveils the intricate dance of electrons within NO2F, revealing the profound influence of resonance on its molecular properties and diverse applications.
Resonance, a fundamental concept in chemistry, allows us to depict the delocalization of electrons within a molecule, providing a deeper understanding of its electronic structure and reactivity. By exploring the resonance structures of NO2F, we gain insights into its unique characteristics and behavior.
Nitryl Fluoride Molecule (NO2F): Draw All Resonance Structures For The Nitryl Fluoride Molecule No2f

Nitryl fluoride (NO2F) is a colorless gas with a pungent odor. It is a powerful oxidizing agent and is used in the production of rocket propellants and explosives. The molecular structure of NO2F is trigonal pyramidal, with the nitrogen atom at the apex and the oxygen and fluorine atoms at the base.
The bonding arrangement within the molecule can be described using valence bond theory. The nitrogen atom has three valence electrons, and each of the oxygen and fluorine atoms has six valence electrons. The nitrogen atom forms a single bond with each of the oxygen and fluorine atoms, and the remaining two valence electrons on the nitrogen atom form a lone pair.
Resonance Structures
Resonance is a concept in chemistry that describes the delocalization of electrons within a molecule. In the case of NO2F, there are two resonance structures that can be drawn. In the first resonance structure, the double bond is between the nitrogen and oxygen atoms, and the fluorine atom is bonded to the nitrogen atom by a single bond.
In the second resonance structure, the double bond is between the nitrogen and fluorine atoms, and the oxygen atom is bonded to the nitrogen atom by a single bond. These two resonance structures contribute equally to the overall electronic structure of NO2F.
Molecular Properties
The molecular properties of NO2F are affected by the resonance between the two resonance structures. The bond lengths in NO2F are shorter than would be expected for a single bond between nitrogen and oxygen or nitrogen and fluorine. This is because the resonance delocalizes the electrons in the molecule, which strengthens the bonds.
The bond angle between the nitrogen and oxygen atoms is also smaller than would be expected for a trigonal pyramidal molecule. This is because the resonance delocalizes the electrons in the molecule, which pushes the oxygen and fluorine atoms closer together.
Applications
NO2F is used in a variety of applications, including:
- As a rocket propellant
- As an explosive
- As a source of fluorine
- As a reagent in organic chemistry
The resonance between the two resonance structures plays an important role in the reactivity of NO2F. The delocalization of the electrons in the molecule makes NO2F more reactive than would be expected for a molecule with a single bond between nitrogen and oxygen or nitrogen and fluorine.
Comparison with Related Molecules, Draw all resonance structures for the nitryl fluoride molecule no2f
NO2F is a member of a family of molecules known as the nitryl halides. The other members of this family are NO2Cl and NO2Br. The resonance structures of NO2F are similar to the resonance structures of NO2Cl and NO2Br. However, the bond lengths and bond angles in NO2F are shorter and smaller than the bond lengths and bond angles in NO2Cl and NO2Br.
This is because the fluorine atom is more electronegative than the chlorine and bromine atoms. The electronegativity of the halogen atom affects the delocalization of the electrons in the molecule, which in turn affects the bond lengths and bond angles.
Q&A
What is the molecular structure of nitryl fluoride (NO2F)?
Nitryl fluoride is a trigonal planar molecule with a central nitrogen atom bonded to two oxygen atoms and one fluorine atom.
How many resonance structures does NO2F have?
NO2F has three resonance structures.
What are the applications of NO2F?
NO2F is used as a nitrating agent in organic chemistry and as a propellant in rocket engines.